LATEST NEWS
February 25, 2026 • 12:20
February 13, 2026 • 12:06
February 13, 2026 • 11:54
EVENTS
January 25, 2022
26 Feb 2026
The European Space Agency (ESA), alongside Europe’s Airbus Defence and Space, the Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research (TNO), and TESAT, have successful demonstrated laser communications between an aircraft and a geostationary satellite over 36,000 kilometres away.

The development is supported by ESA’s Optical and Quantum Communications – ScyLight programme, within the Advanced Research in Telecommunications Systems (ARTES) programme. ScyLight addresses the development, demonstration and utilisation of innovative optical and quantum technologies for satellite communications through system studies and market analyses in partnership with Industry. Fulfilling this mandate, UltraAir’s technology paves the way for secure, gigabit per second–speed communications with low probability of interference or interception.
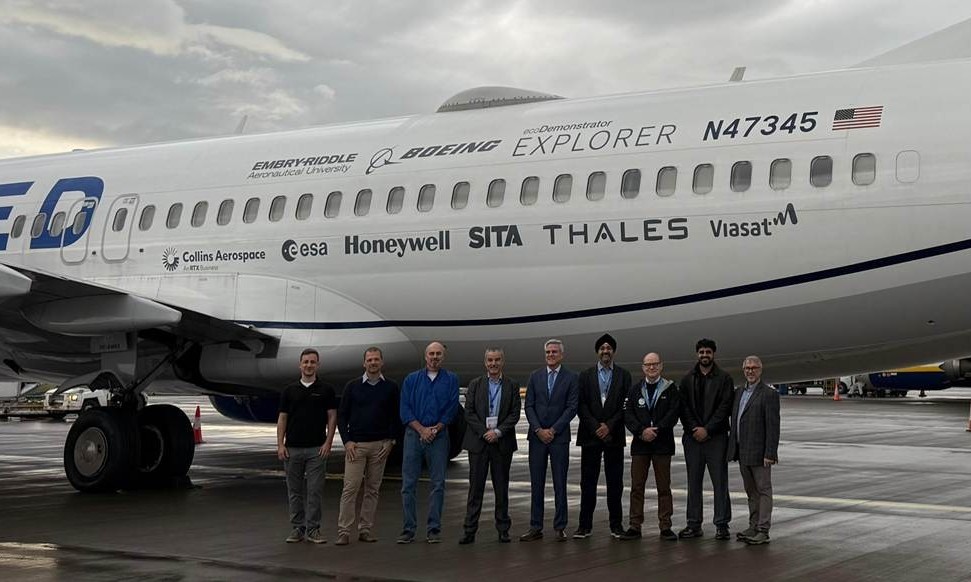
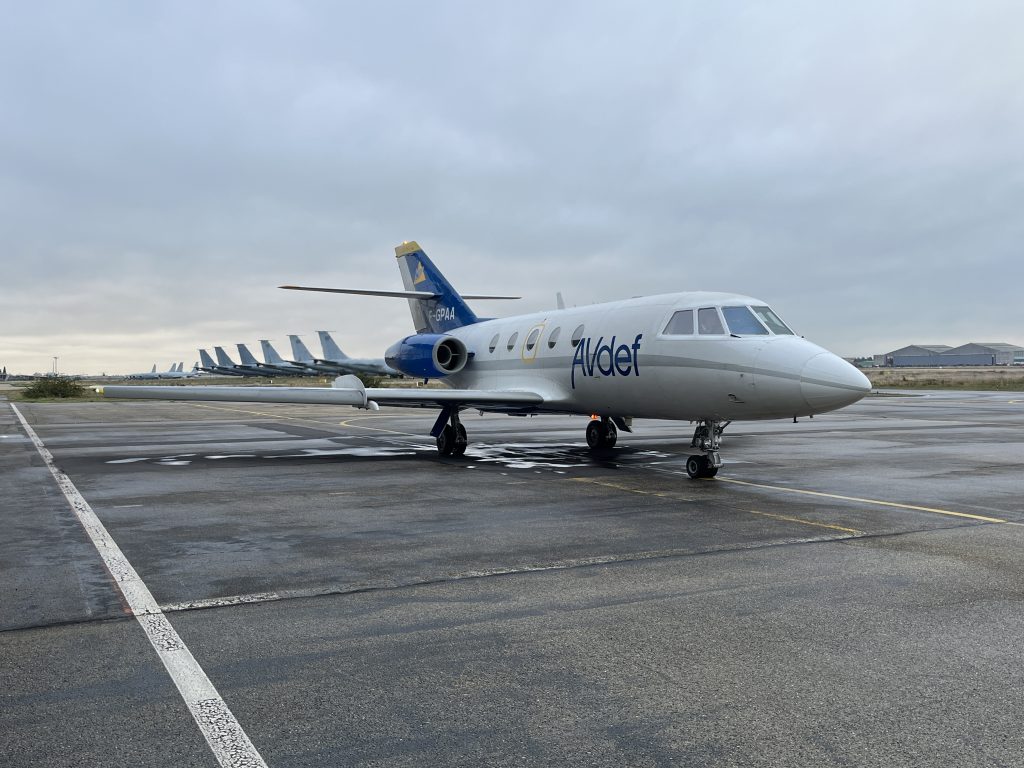
In a series of flight tests from the Nîmes Airport in France, the jet aircraft equipped with Airbus’ UltraAir laser communication terminal established and maintained a secure laser link with its counterpart in geostationary orbit. On the aircraft, the UltraAir terminal’s mechanical and optical control technology – needed to achieve a stable laser link – was developed by TNO, while its free-space optical link was provided by Airbus subsidiary, TESAT.
Together, these advancements allowed UltraAir to connect with a TDP–1, a testbed for the implementation of optical data links equipped onboard the Alphasat satellite. The TDP-1 Laser Communication Terminal is owned by the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and is operated by TESAT, in collaboration with ESA.

Optical data links have the potential to enable satellites to rapidly and securely transmit complete data sets in a single burst, a significant improvement over legacy Radio frequency (RF) systems. The UltraAir demonstration flights tested acquisition and tracking abilities for optical links from a moving platform – rather than a static ground station – and established a seamless performance: a bit error free, coherent data rate of 2.6 gigabit per second that remained uninterrupted for several minutes.
This advancement has both civilian and defence applications, providing a secure alternative to RF satellite communications. RF has historically been the backbone of satellite communications, but it can be intercepted, jammed and disrupted by user proliferation and adverse weather – decreasing the integrity and security of data transmissions. In defence, laser communications could help overcome the challenge posed by clouds in multidomain operations and make it harder to intercept communications. In civilian applications, it could enable high–speed data connections with mobile platforms such as passenger airliners, cars and ships to keep passengers connected.
“This achievement demonstrates how optical communications can transform secure connectivity for our Member States. Particularly by working to resolve the technical challenges that come with establishing fast laser communications, capable of evading interference and detection in demanding conditions,” said Laurent Jaffart, Director of Resilience, Navigation and Connectivity at ESA. “Collaboration drives innovation, and this milestone will strategically deliver benefits to future missions, where speed and security of data transmission is paramount. For Europe and beyond.”
“Establishing laser links between moving targets at this distance is technically very challenging. Continuous movements, platform vibrations and atmospheric disturbances require extreme precision,” said François Lombard, Head of Connected Intelligence at Airbus Defence and Space. “This milestone is a further development of our long successful laser communication history; it opens the door to a new era of laser satellite communications to meet defence and commercial needs in the next decades.”
“This breakthrough proves that our industry strengthens Europe’s security and its autonomy by leading strategic technology in the field of secure laser communications,” said Kees Buijsrogge, Director of Space at TNO.
“Optical communications between airborne users and satellite networks, like ESA’s High-thRoughput Optical Network (HydRON), are high on ESA’s agenda,” said Harald Hauschildt, Head of ESA’s Optical and Quantum Communication Office. “High-data rate, low-latency links that connect High-Altitude Pseudo Satellites (HAPS) and aircraft are equally demanded for commercial and resilience driven applications.”
The project was co-funded by Airbus and TNO, with support from the Netherlands Space Office (NSO) and the German Aerospace Center (DLR) as part of ESA’s Optical and Quantum Communications – ScyLight programme.