PAGE CONTENTS
Objectives
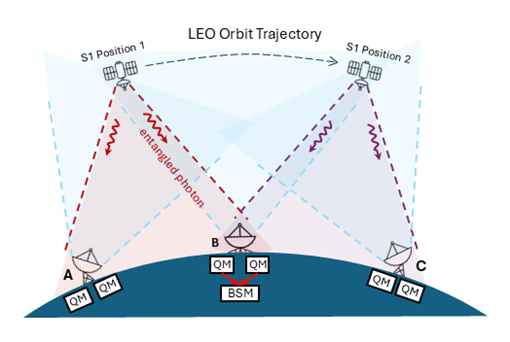
Quantum networks promise to provide huge benefits in the fields of quantum computing, quantum sensing and secure quantum communication. As with their classical counterparts, these new quantum networks will require the ability to store and retrieve data. A quantum memory is a device that can store arbitrary quantum states of light, such as photonic qubits or entanglement, and retrieve that quantum state on-demand at a user-defined time. Achieving this requires the efficient, coherent, and reversible mapping of the input optical mode to and from a single or collective long-lived matter excitation.
For satellite-based quantum networks there are a number of considerations when selecting a memory platform. For example, the use of low-Earth orbit sets a fundamental lower limit on the storage time needed for the memory. Ideally, quantum memories must also be able to store multiple qubits in order to achieve a useful rate of quantum information exchange and interface with existing network infrastructure. Most quantum memories do not typically perform well across all these requirements and hence compromises must be made. The objective of the QMC project is to identify a candidate platform that best meets the requirements and thus provides the most promising opportunity to realise a satellite-based quantum memory in the future.
Challenges
Key challenges of the QMC project include:
- Determining which aspects of the quantum memory performance are the most significant and should be prioritised;
- Assessing the potential for development of existing quantum memory technology which could lead to significant gains in performance.
System Architecture
The QMC quantum memory proposal is based on a rare earth ion crystal, held at low temperature (1.5K) and operating in a high (>1T) magnetic field. A spin-wave atomic frequency comb (AFC) protocol, within an impedance matched cavity, is used to create the photon storage.
Plan
The project is divided into several stages:
- Define a reference scenario in which the quantum memory will operate;
- Determine the technical specification required for the memory and assess the current state of the art across existing quantum memory platforms;
- Select a target platform and establish a potential baseline concept and assess its feasibility.
Create a technology development plan and roadmap to raise the Technology Readiness Level (TRL) of relevant peripheral technology
Current Status
Within the QMC project we have outlined the reference scenario for a quantum memory and carried out a critical assessment of existing protocols and platforms. A trade off analysis has been performed to select our candidate platform with the results informing our baseline quantum memory concept. This baseline concept has been developed to explore improvements to existing systems which could potentially enhance memory performance. A research and development roadmap has also been devised for future hardware development.
Companies

