PAGE CONTENTS
Objectives
The BGAN-extension (BGAN-X) Phase 1 programme was established in August 2003 to undertake the design, development, prototyping and validation of several new classes of satellite mobile terminals.
The programme led to the development and commercial availability of a range of mobile terminal types that extended the baseline BGAN system into land vehicular, maritime and aeronautical sectors. These new terminals enabled Inmarsat and its partners to expand the traditional customer base and penetrate into new market though the advent of smaller, higher capability and more cost effective mobile terminals than Inmarsat had previously been able to offer to these markets.
The programme objectives also included the evaluation of market opportunities for multicast service for efficient delivery of data to multiple terminals simultaneously. This programme objective included the development of system architecture and operation, culminating in the validation of the BGAN multicast service concept via a Proof of Concept system.
Background
The BGAN system was developed to provide 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) services to portable mobile terminals via the Inmarsat-4 satellites, offering up to 492kbps to the highest capability mobile terminals. BGAN delivers ‘always-on’ Internet Protocol services, telephony and ISDN. Using the Inmarsat-4 (I-4) satellites and a new generation of small, light user equipment BGAN delivers a higher data rates at lower costs than any previous Inmarsat system. The land portable terminals at service introduction are shown below. BGAN entered service in Dec 2005.
Figure 1: BGAN Land Portable Terminals available at service launch
 |
 |
| Class 1 User Terminal | Class 2 User Terminal |

Class 3 User Terminal
The I-4s are some of the largest geostationary satellites in service. The dry mass of the spacecraft is estimated at around 3400kg, with a separation mass in the region of 6000kg. They are based on Astrium’s Eurostar 3000 platform and contain a 9m unfurlable reflector that provides a global beam, 19 regional beams, and approximately 228 spot beams.
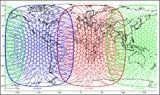
The BGAN system maximises the use of this satellite capacity by reallocating it dynamically to meet demand, to ensure that bandwidth is always available when and where users need it. The first two Inmarsat-4 satellites were launched on 11 March and 8 November 2005. The third Inmarsat-4 was launched on 18 August 2008, enabling Inmarsat to provide BGAN services worldwide, with the final planned constellation shown below.
Figure 2: Inmarsat-4 narrow spot beam coverage
BGAN supports circuit switched (CS) and packet switched (PS) services. Circuit switched include dial-on-demand digitised 4.8kbit/s voice and 64kbit/s ISDN. Packet switched services include standard (or background) IP, which is charged by volume and streaming mode IP which provides guaranteed Quality of Service and is charged by time. In addition Short Message Service is supported. The user can access CS & PS services simultaneously, and can have up to 11 Packet Data Protocol (PDP) contexts established.
Challenges
New Service Capabilities Proven
One of the key issues that was to be addressed by the BGAN-X Phase 1 programme included the effective operation of all mobile terminal classes in a range of environmental conditions, resulting in the successful commercial deployment of the new mobile terminal classes.
BGAN Extension Phase 1 also developed the concepts for efficient delivery of IP-Multicast traffic over a 3GPP network. Multicast can offer significant satellite resource savings when distributing information to large user groups, thereby providing significantly improved value to Inmarsat, its service providers and end users.
The BGAN Multicast design is very efficient in that traffic can be carried on the shared bearers active in each spot beam, and does not require separate bearers to support the service. Information is only transmitted in spot beams with terminals authorised to receive the content. Non-real time applications include weather and chart updates, database replication, software updates and video downloads. These concepts were validated in a Proof-of-Concept configuration, involving fully emulated satellite and terrestrial networks supporting real multicast content-distribution applications.
Real time multicast applications such as netted voice, whiteboard collaboration and Netmeeting-type conferencing were not considered in BGAN-extension Phase 1, and are now the subject of BGAN-extension Phase 2. It is anticipated that a commercial roll-out of both content-distribution and real-time multicast applications will take place upon the conclusion of BGAN-extension Phase 2.
Plan
Current Status
Ongoing related activities at the end of the Project
The standardisation of the BGAN-X waveforms was initiated as part of the BGAN-X Phase 1 programme, and this activity is continuing in ETSI, expected to conclude during 2009. This is considered a key enabler for the development and deployment of future safety service platforms using the Inmarsat satellites.
Current strategy is to work with the manufacturers to further develop the mobile terminals for higher volume manufacturing, and to transition use of the legacy Inmarsat systems to BGAN to support higher capacity in the Inmarsat-4 spot beams. Inmarsat has a strong legacy of providing safety-of-life services, and there is significant interest in the possibility for BGAN to become the platform for future safety services.
Inmarsat is currently endeavouring to develop service and product concepts that will facilitate the deployment of high reliability and high availability services tailored to meeting these requirements. This includes the development of extensions to the air-interface, extensions to the protocols and new infrastructure. It is anticipated that some of this work will be undertaken with the support of future ESA ARTES programmes.
Documents
Companies