PAGE CONTENTS
Objectives
The CVICS objective was to create a solution for the distribution of VOD content and catch up TV services which targets rural areas and regions where no high speed broadband solutions are available. The solution also provided a new and valid business opportunity for network providers, content providers and end users.
Challenges
There were number of challenges in the CVICS project:
- The complexity present in the design and development of a full end-to-end solution.
- The parallel design of the CVICS subsystems by two different companies required close collaboration between the team members.
- The provision of a system able to engage the end-users involved in the trial phases.
- The provision of appealing content to trigger a high level of interest in the end-users involved with the pilot.
- The provision of quick and efficient communication with the end-users during the trial phases.
Plan
The Project plan was divided into 6 phases:
- User Requirements.
Definition of the use cases and the requirements for:
- service operator;
- satellite provider;
- content provider;
- end-users.
- Design and Specification.
Overall system design including a detailed design of each of the components that constitute the CVICS system.
- Development of the System Components.
- During this phase the system components were built. This involves software development, the procurement of the hardware, and the setup of the satellite gateway. During the development all system components were tested in a lab environment.
- Integration.
The integration phase aimed to verify the full system functionality via end-to-end testing.
- User Trials.
After successful integration, the CVICS pilot was run. This involved 10 end-users that evaluated the CVICS product from an end-user perspective.
- Decommissioning and results evaluation.
During the pilot, users provided feedback to analyse and evaluate the technical and commercial aspects of CVICS. Additional usage-logging of the STB terminals was also gathered for evaluation. Following this, a 2nd iteration of the business case and a commercial feasibility study was conducted. Finally, based on this, a roadmap for the future of the CVICS system was created.
Current Status
- The CVICS solution has been fully implemented and was demonstrated at the PQR meeting on 21st November 2013, the demonstration and tests included
- Validation of the STB
- User interface
- Content play out
- Content reception
- Validation of the media distribution centre
- Content management
- Ingest and update of content
- Validation of the satellite uplink (cross-strap solution)
- Validation of the connected Android device
- Installation
- Browsing of content
- Play out/Download of content
- Pilot participants were recruited and the equipment was installed at the user premises
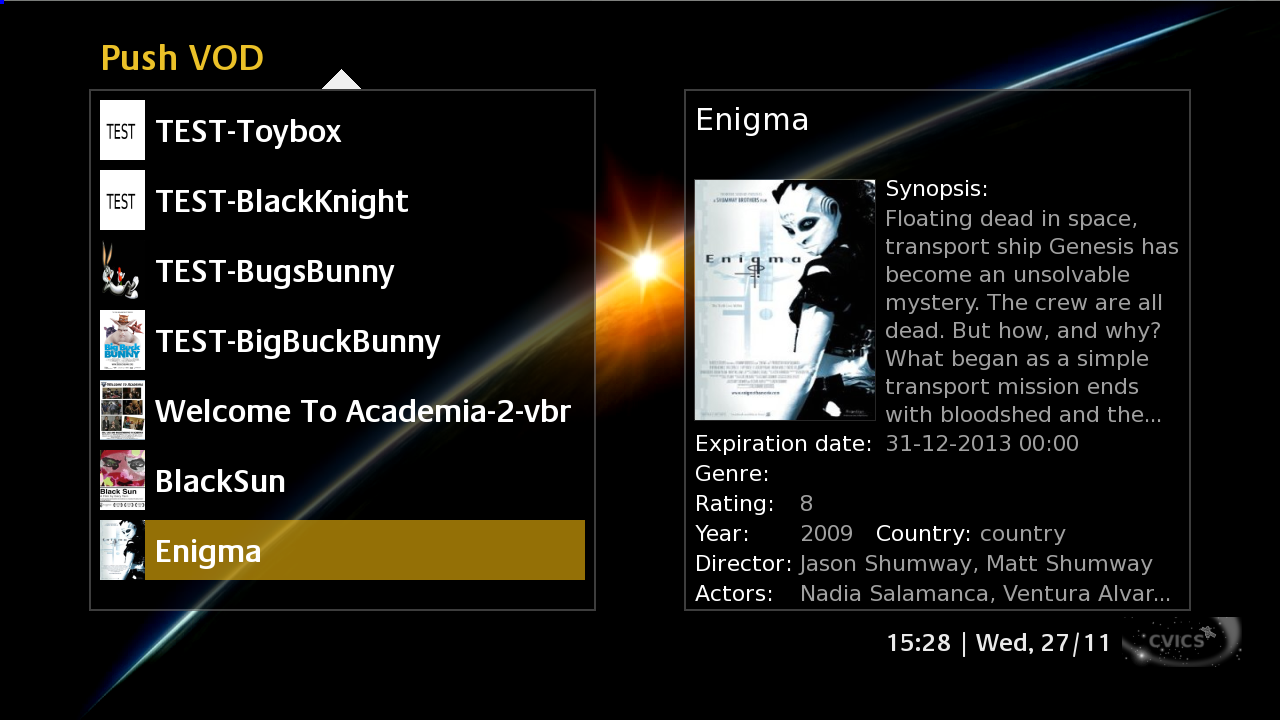
- The new Ku band antenna integration was completed by end of 2013, and successfully validated by ESVA test on 10 Feb 2014 with the support of the Redu Earth Station.

- The pilot started on March 5th 2014 involving users based in UK, Spain, Portugal and Cyprus and two monitoring stations, one in London and one in the Eindhoven.
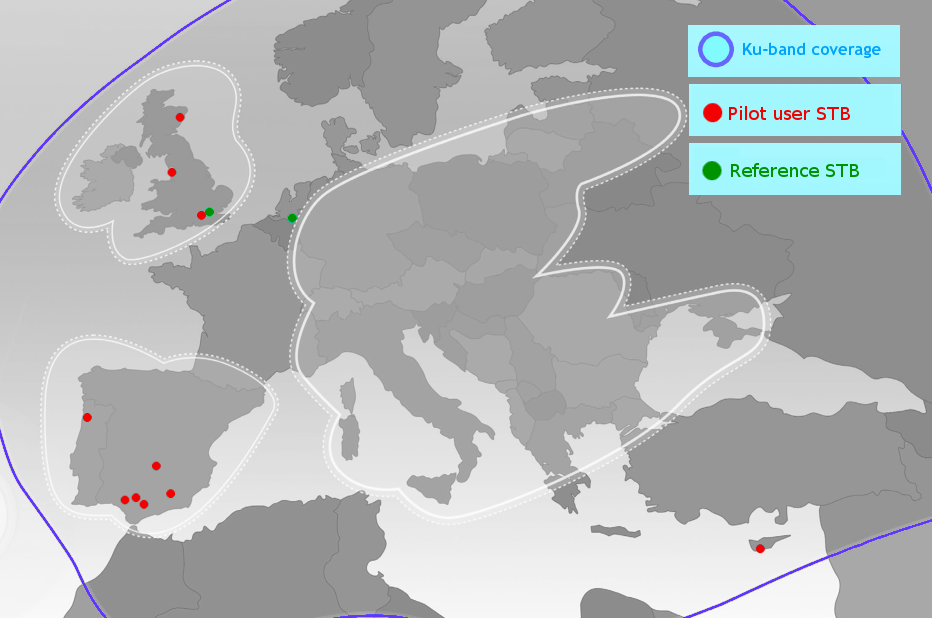
- The pilot’s duration was three months, the users were provided an average of 3 new movies per week, and they had to fill a weekly questionnaire to provide feedback on their experience.
- With the exception of a small issue that impacted the modulator in the 3rd week of operation, the pilot went smoothly.
- The Pilot was completed on June 5th and the project final review took place on July 16th.
Results
From a technical point of view, the system meets the expectations.
Overall, the users were satisfied with the system, providing valuable feedback with respect to content and applications. The analysis of the results provided the following conclusions:
- Content is the King – viewers are saturated by a very extensive media offer and only exclusive content allows to capture their attention.
- A reliable CA/DRM is mandatory for any kind of commercial deployment to allow the acquisition of content from the major studios.
- Users are willing to pay for a PVOD service, but rather as part of a DTV bundle.
- Users need to be “educated” on how to operate a PVOD system (do not power down the STB during night time).
- Subscription based VoD seems to be the more popular model.
- 2nd screen (tablet) is becoming increasingly important
Companies


