PAGE CONTENTS
Objectives
This study investigates technical solutions that will increase the flexibility of telecommunications payloads with specific focus on C/Ku and Ka-band multi-beam architectures. Flexible technology options under study include flexible MPMs, digital transparent processing, MPAs, agile downconverters, reconfigurable filters, and switching options. The study will identify the most promising solutions for development and provide a roadmap covering a ten year timeframe.
The objectives are:
- To categorise and quantify flexibility at telecommunications repeater level.
- To identify the technologies, types of equipment and related key performance requirements for future flexible telecommunication satellite repeaters.
- To quantify the benefits of new repeater architectures and equipment types with respect to conventional repeater designs.
- To provide a roadmap for critical repeater technology and equipment implementation covering a 10 year time frame, taking into account current and targeted performances.
Challenges
The challenge for operators and manufacturers is to achieve improved repeater flexibility and performance without significant impact to complexity and cost. Satellite procurement schedules and technology risk profiles must also be consistent with commercial satellite communication service objectives.
Flexibility in-orbit is desirable as it can allow for increased capacity, reduction of commercial risk and allow for late changes to mission requirements. More generic design should also allow manufacturers to offer competitive benefits.
There are a number of flexible payload technologies which are or are becoming commercially available. The increased equipment cost or potential impact to performance compared to conventional equipment must be compensated by an equivalent return to the operator.
This study aims to assess the benefit of flexible repeater architectures and technologies in a bottom-up approach to identify solutions that will provide the greatest commercial return.
Plan
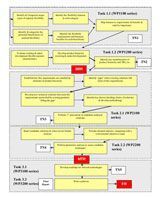
The Study is divided into three phases.
Phase 1 aims to identify and categorise flexibility requirements, beneficiaries and perform a ranking. In addition Phase 1 includes a survey of the current status of flexible repeater architectures and technologies.
Phase 2 performs a comparative analysis of the benefits of increasing levels of flexibility within the repeater architecture.
Phase 3 consolidates the work undertaken in order to provide the roadmap.
The above figure shows the logic of the study and the sequence of the tasks.