
-
StatusOngoing
-
Status date2024-03-25
-
Activity Code3A.106
Preliminary analyses have shown that the NB-IoT standard can be used by satellite systems in non-geostationary orbits under certain constraints. However, to enable the integration of user sensors employing this technology, it is necessary to develop an on-board evolved node B (eNB) capable of using a standard not originally conceived for satellite communications with adaptation and additional features dictated by the scenarios. Moreover, the eNB is preferably compatible with small satellites platforms in terms of mass, power and volume since these platforms are usually the ones selected to provide M2M/IoT services. Finally, it is also important to develop and propose UU (radio interface between UE and eNB) adaptations that would allow maximizing the efficiency of a satellite system.
The goal of the project is the development of a demonstrator in which communication between an NB-IoT User Equipment and an eNB adapted for satellite communications is functionally verified.
The state-of-the-art technology for NB-IoT is critically revised, referring to integration with satellite systems and associated technical requirements expected by the demonstrator.
The project aims at developing a demonstrator where the communication between a NB-IoT UE and the adapted eNB is functionally verified. The main challenges are:
-
identification of the scenarios suitable for NB-IoT via NTN and what are their impacts in terms of key architectural strategies;
-
identification of adaptations needed to enable the operation of satellite links for NB-IoT for both Access Stratum (AS) and Non-Access Stratum (NAS);
-
development of a satellite RAN, including a User Equipment (UE), an RF and baseband processing unit and an eNB;
-
Functional and performance verification of NB-IoT over satellite.
Development and validation of the adaptations to the UU’s PHY, MAC, RLC, PDPC, and RRC layers to make the NB-IoT radio standard viable over satellite.
Development of an on board eNB capable of supporting the adapted 3GPP NB-IoT standard within the mass, power, and volume constraints of a small platform (<12U). The demonstrator is capable of emulating different scenarios as well as the main limiting factors in the telecommunications channel, with reference to doppler shift/rate, mobility, possible shadowing/multipath, in order to assess performance under realistic conditions.
The aim of the project is the development of a Testbed to validate a communication between an NB-IoT User Equipment (UE) and an eNB, considered installed on board a LEO satellite, by emulating the impairments introduced by the satellite environment (attenuation, delay, doppler shift). The Testbed consists of 2 ETTUS B200, which implement the UE and the eNB. A SW is installed on these platforms to emulate the NB-IoT protocol stack, customized to be able to manage the specificities introduced by satellite communication, in particular the management and compensation of the Doppler Shift.
The emulation of the impairments is performed through a TASI’s proprietary Channel Emulator, made available for testing activities, which is able to simulate the impairments following a specific profile, representative of the movement of a LEO satellite.
Exploiting an Adalm Pluto, it is possible to emulate the presence of NB-IoT traffic, managed through pre-recorded sequences defined in the simulation phase.
The System Architecture is shown in the following picture:
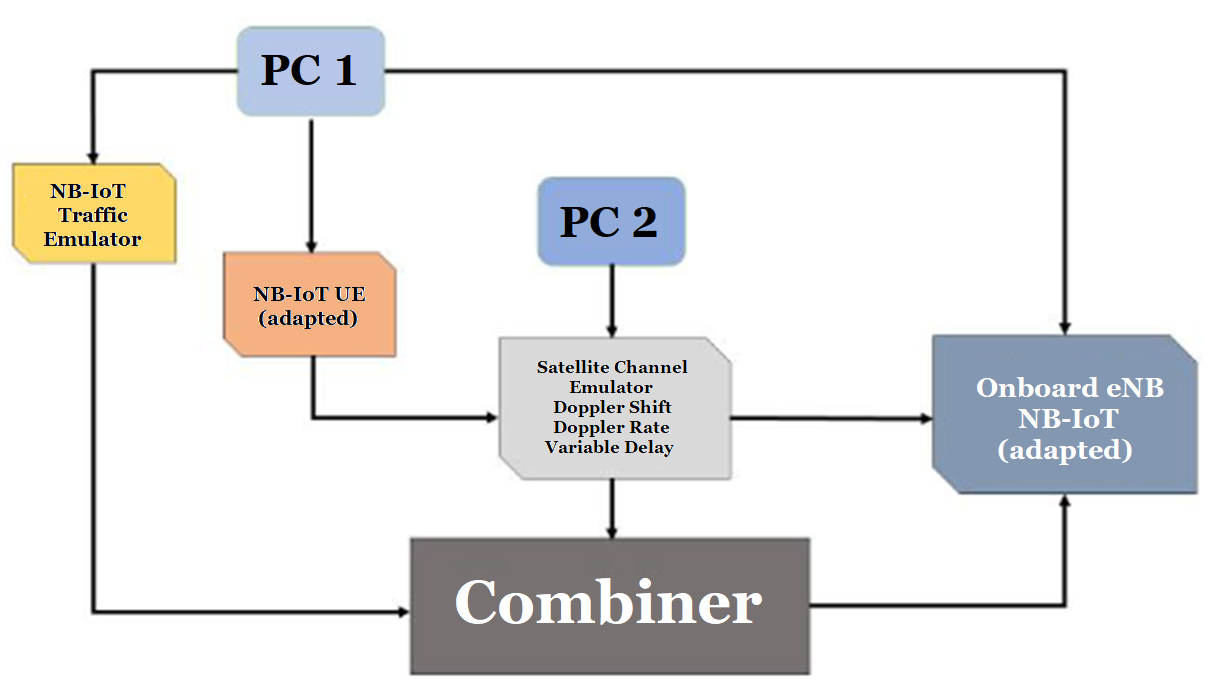
The main sub-systems are:
-
NB-IoT Traffic Emulator: to emulate the traffic generated by several UEs.
-
NB-IoT Adapted UE: is an NB-IoT terminal emulator based on an SDR with UU interface adaptations.
-
Channel Emulator: to emulate all the impairments caused by LEO satellites. In particular, is able to introduce variable delay, variable Doppler Shift, Phase Noise, Fading.
The project foresees the following relevant milestones:
-
MS1: Preliminary Operation Scenario Requirements and acceptance of all related deliverables.
-
MS2: Technical Requirements (traffic emulator, NB-IoT UE, Channel Emulator, On-board eNodeB Prototype) and acceptance of all related deliverables.
-
MS3: Testbed Implementation and acceptance of all related deliverables.
MS4: Results, Roadmap and acceptance of all related deliverables.
The activities started on 1st April 2020.
The milestone MS1 has been achieved with the completion of WP1 relating to scenarios definition and challenge identification.
The milestone MS2 has been achieved with the completion of work packages WP2 and WP3, concerning UU Interface and Testbed Requirements.
The milestone MS3 has been achieved with the completion of the activities concerning the Testbed Design, Development and Verification and the Test Plan definition.
The Final Review has been achieved at the end of the overall activities.





