
Iris contribution to ATM benefits:

The satellite-based Iris system is fully certified and operational as a key element in a successful European implementation of Data Link Services for Air Traffic Management (ATM) in Europe and beyond, and is now looking at becoming a global solution.
WHAT IS IRIS?
Iris is a Data Link Service (DLS) satellite system, funded and promoted by the European Space Agency (ESA) in partnership with Viasat and industry.
Iris is based on Viasat’s existing infrastructure:
• I4 geostationary satellites (I6 coming soon)
• SwiftBroadband – Safety (SB-S) technology that is already approved for oceanic use and will be extended for use in continental airspace.
Iris provides Data Link for Air Traffic Service (ATS), referred to as ATN B1, ATS B2, ACARS (CPDLC & AOC), voice and Airline Operational Communications (AOC), including IP connection for EFB, in one single system.
Today Iris is the only mature technology able to complement the existing terrestrial solution (VHF Data Link Mode 2 or VDL-m2), offloading the excess traffic in a multi-link (or dual-link) fashion.
In line with the Single European Sky ATM Research (SESAR) Joint Undertaking (SJU) ATM Master Plan, Iris was designed not only to comply with standards and performance requirements for ATS communications (RCP 130 and RSP 160 for ATS B2), but also to enhance safety and security and to support data-hungry AOC services. It is easily scalable with the potential to meet future needs.
An Iris capacity study, carried out by the Iris consortium in line with SESAR Deployment Manager assumptions, has indeed confirmed that Iris has sufficient capacity, by large margins, to support both the volume of data expected to be offloaded from VDL2 and the increased traffic anticipated in the coming years.
Furthermore, Iris supports ADS-C applications (extended projected profile - EPP), as key enablers for i4D to deliver route optimisations, reducing delays and avoiding air traffic congestion. Consequent fuel savings and related reductions in CO2 emissions result in a much better flight efficiency, and a better experience for passengers.
Overall, Iris represents a secure, reliable and cyber resilient solution, with cyber resilience to malicious attacks, and meets the availability and performance requirements required to support ATS services. The satellite offers immediate coverage across Europe and has scalable potential to become a global service, as well as supporting data-hungry services.
A high-level diagram of the Iris end-to-end system is shown below, highlighting the highly secured Iris link, including authentication and message integrity features.
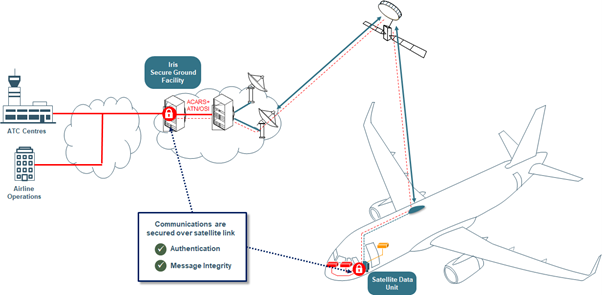
Iris is integrated in the Common European ATM infrastructure, developments are on-going to enable compatibility with ATN-IPS standards and technology.
WHY IRIS?
European airspace is one of the most congested in the world. Despite the heavy impact of COVID-19 on the world economy - including on the aviation sector - the number of flights returned to about 2019 levels in 2023 and is still expected to reach the anticipated 50% forecast increase by 2050.
The existing terrestrial infrastructure (so-called VDL-m2) will soon face a capacity shortage.
ATM modernisation is essential if Europe is to achieve the digital transformation and green deal goals prioritised by the European Commission.
Developed for ESA by a world-class industrial consortium, led by Viasat, Iris contributes to the European Commission’s Aviation Strategy, unlocking benefits for the aviation community worldwide. Iris will contribute to the modernisation of ATM, while increasing flight safety and operational efficiency, as is also highlighted in the SESAR “ATM Master Plan”.
Furthermore, Iris will play a key role if ATM modernisation is to achieve the European Green Deal target for a carbon neutral aviation by 2050.
Iris CO2 savings are in the order of several million tonnes of CO2 per year in Europe over the 2024-2040 timeframe. This will result in cumulative savings of up to 40 million tonnes of CO2 by 2040.
View/download green paper: Iris Green Value - How ESA is harnessing satellite technology to reduce aviation emissions
Additional benefits for the airlines derive from real-time information sharing, which will enable aircraft health monitoring and optimised inventory, resulting in optimised maintenance scheduling.
Iris therefore represents a win-win solution: airlines will harness more sustainable flights, reducing excess fuel with resultant cost reduction, while passengers will experience fewer delays and an improved service, together with a lower footprint for their air-travel.
STATUS
The results achieved so far draw on the involvement of leading European institutional stakeholders (The European Commission, SESAR Joint Undertaking, SESAR Deployment Manager, EASA and EUROCONTROL).
ESA is committed to continuing this cooperation with European institutions in support of the Single European Skies policy, set by the European Commission. To this end, ESA has signed a Memorandum of Cooperation with the SESAR Joint-Undertaking (SJU), the SESAR Deployment Manager (SDM), Eurocontrol and EASA to guarantee the Iris is compliant with the required standards and regulations.
In July 2023, ESSP has been certified by EASA as Iris Service Provider. This is the first pan-European communication certification in the aviation history.
About 19 ANSPs have so far joined the pre-commercial flights with easyJet. Since January 2024 several easyJet aircrafts are flying using Iris operationally. By July 2025 more than 8,000 flights have been carried out (and counting) with very good performances. ITA Airways has joined Iris flights as well in July 2025 and other airlines are in the pipeline to join.
Next step is to enhance Iris to adopt the recently approved IPS standard to be used by Boeing aircrafts (which represents about 50% of flights in Europe and worldwide) and to expand Iris adoption beyond Europe (e.g., USA and Far East).

Related links:
Iris Green Value - How ESA is harnessing satellite technology to reduce aviation emissions
FEATURED OPPORTUNITIES
Space Systems for Safety and Security (4S) Applications
31/12/2025
View details
NEWS AND EVENTS
Italian airline signs up for space-enabled flights
Passengers flying on Italy’s national carrier ITA Airways will experience fewer flight delays and greener travel thanks to pilots being able to use satellites to route their planes.
The ESA-backed Iris for aviation system connects pilots…
easyJet signs up for space-enabled digital skies
Passengers on board commercial airline easyJet will speed to their destinations faster and greener, thanks to an ESA-backed initiative to digitalise the skies.
Iris system to digitalise airspace goes global
A space-enabled system to help clear congested skies while reducing carbon emissions is going global, following a deal signed today between satellite communications provider Inmarsat and ESA.
Satcom Maturity and Deployment
Satellite technologies are evolving and new modern and secured communications are being developed that offer new opportunities to meet current and emerging aviation requirements.
Iris takes a step closer to becoming a reality for air traffic management
A workshop on using a new satellite-based air-ground communication system for air traffic management took place at Brussels airport on 2 OctA workshop on using a new satellite-based air-ground communication system for air traffic management took…
Satellite-enabled air traffic control system takes to the skies
Air travel is set to become safer, swifter and more environmentally friendly thanks to the introduction of space-based technologies.
The Future in Aviation: Iris, a reality for Air Traffic Management
On Wednesday 2 October 2019, the European Space Agency and SESAR Deployment Manager are organising an event to update all ATM stakeholders on Iris, a new satellite-based air–ground communication system for Air Traffic Management.…
Space tech poised to make air travel greener & more efficient
13 Mar 2019 - Several national air traffic control organisations have agreed to trial the commercial system, including those of Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Switzerland and the UK.
Iris System Takes first flight
17 July 2018 - Europe is one step closer to a safer, cleaner sky, as the Iris aviation satcom system completes its first set of test flights.
SESAR Deployment Manager and European Space Agency sign MoC
On 19 Jul 2019, SESAR Deployment Manager and the European Space Agency (ESA) have signed a Memorandum of Cooperation marking the start of the collaboration between both organisations to coordinate between the deployment of the satellite-based…
Preparing for air traffic control via satellite
20 Dec 2016 – Flight trials were recently undertaken by ESA and Inmarsat in the next stage of the ARTES Iris Precursor programme to deliver high-capacity secure digital data links via satellite.
ESA signs Memorandum of Cooperation with SESAR
15 Sept 2016 - ESA and the SESAR Joint Undertaking have signed a Memorandum of Cooperation to work more closely in modernising air traffic management through satellite-based communications.












