In this page you can search all ARTES except ARTES 20 IAP, which can be found on Business Applications - Projects.
Please click on the + symbol to expand the Filter By ARTES Elements to narrow your search. If you are looking for a specific element select from the list provided and click on the Apply button to start the search and display the results.
Displaying 361 - 400 of 1740
CANOPIES
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
DeSPPAAM

Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
NON-GEO 5GCBH

Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
GR740 PBGA
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
Hybrid Connectivity as a Service (HCaas)

Status date:
Prime Contractor
HTS Free Hopper

Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
RPAS-HAPS
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
WAKA DOCON
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
PERSILS

Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
xSPANCION
Status date:
Prime Contractor
SatNEx V

Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
HPSA
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
SCNE
Status date:
Prime Contractor
5G-HINTS
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
Romantica

Status date:
Prime Contractor
MSMO
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
Spectrum Monitoring Mission Feasibility Assessment
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
Ge.Lo.Sy.

Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
AIDA
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
MRC-SAT
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
MTAILS CCN
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
Development of the RF Equipment for the Next Generation of Digital Processors
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
Flexible Compact Array Stack Rotation And Release Mechanism
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
CONSTELLATION
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
KaTropical
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
DTP NG
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
HIGH THROUGHPUT SATELLITE (HTS) GATEWAY Q/V - BAND FEED ANTENNA
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
SATBETT-5G
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
IOT SATBACK

Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
Development and in orbit validation of Digital Processed Payload (without converters) (ATLAS)
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
SatcomWeather 2
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
LCUT
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
Esa-DTH

Status date:
Prime Contractor
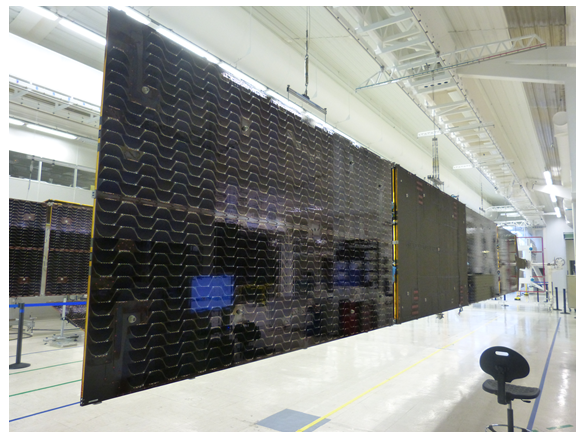
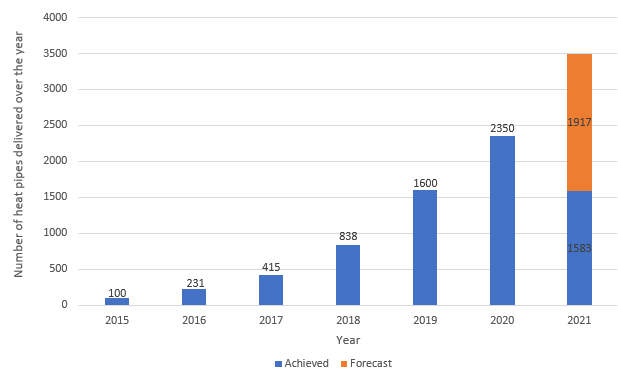
Heat Pipes Development, Qualification and Industrialisation
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
OneSat eDPS

Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
SCFC

Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
HV on PCB

Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
QDEV
Status date:
Prime Contractor
Subcontractors
On-Board Guidance Optimization for Electric Propulsion Orbit Raising
Status date: